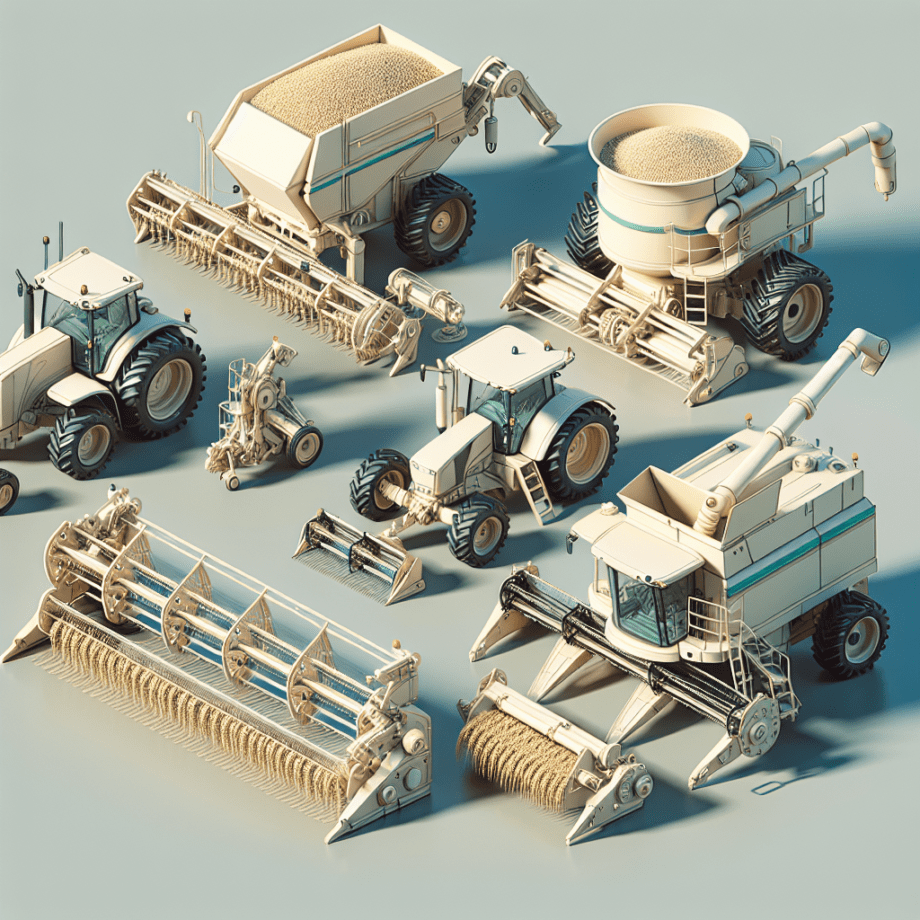
Rice farming is a critical agricultural activity that feeds billions of people worldwide. The efficiency and productivity of rice farming have been significantly enhanced by the development and use of specialized machinery. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of machinery used in rice farming, their functions, and the benefits they bring to the agricultural sector.
Types of Machinery Used in Rice Farming
Tractors
Tractors are the backbone of modern rice farming. They are versatile machines used for a variety of tasks, including plowing, harrowing, and leveling the fields. Tractors come in different sizes and power ratings, allowing farmers to choose the right model based on the size of their fields and the specific tasks they need to perform.
Modern tractors are equipped with advanced features such as GPS for precision farming, automated steering systems, and real-time data collection. These features help farmers optimize their operations, reduce labor costs, and increase overall productivity.
Plows
Plows are essential for preparing the soil for rice planting. They are used to turn over the soil, burying crop residues and weeds, and creating a suitable seedbed. There are several types of plows used in rice farming, including moldboard plows, disc plows, and chisel plows.
Moldboard plows are commonly used for primary tillage, as they can turn over large amounts of soil. Disc plows are more suitable for breaking up hard or compacted soil, while chisel plows are used for deep tillage without turning the soil completely.
Seeders and Transplanters
Seeders and transplanters are crucial for the efficient planting of rice. Seeders are used to sow rice seeds directly into the field, while transplanters are used to transplant rice seedlings from nurseries to the field.
Mechanical seeders can significantly reduce the time and labor required for planting, ensuring uniform seed distribution and optimal plant density. Transplanters, on the other hand, help in maintaining consistent spacing between plants, which is essential for maximizing yield and reducing competition for nutrients.
Harvesters
Harvesters are used to efficiently and quickly harvest rice crops. There are two main types of harvesters used in rice farming: combine harvesters and reapers.
Combine harvesters are multifunctional machines that can cut, thresh, and clean the rice in a single pass. This significantly reduces the time and labor required for harvesting. Reapers, on the other hand, are simpler machines that cut the rice stalks, which are then manually threshed and cleaned.
Threshers
Threshers are used to separate the rice grains from the stalks and husks. They can be standalone machines or integrated into combine harvesters. Threshers come in various sizes and capacities, allowing farmers to choose the right model based on their needs.
Modern threshers are designed to minimize grain loss and damage, ensuring high-quality rice. They are also equipped with features such as adjustable settings for different crop conditions and easy maintenance.
Benefits of Using Machinery in Rice Farming
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The use of machinery in rice farming significantly increases efficiency and productivity. Machines can perform tasks much faster and more accurately than manual labor, allowing farmers to complete their work in less time and with fewer resources.
For example, a combine harvester can harvest several acres of rice in a single day, a task that would take several days if done manually. Similarly, mechanical seeders and transplanters can plant rice more uniformly and at a faster rate than manual methods.
Reduced Labor Costs
Labor costs are a significant expense in rice farming. The use of machinery can help reduce these costs by minimizing the need for manual labor. Machines can perform tasks that would otherwise require multiple workers, allowing farmers to save on wages and other labor-related expenses.
Additionally, the use of machinery can help address labor shortages, which are a common issue in many rice-growing regions. By relying on machines, farmers can ensure that their operations continue smoothly even when there is a lack of available labor.
Improved Crop Quality
Machinery can help improve the quality of rice crops by ensuring that tasks are performed more accurately and consistently. For example, mechanical seeders and transplanters can ensure uniform seed distribution and plant spacing, which can lead to healthier plants and higher yields.
Similarly, modern threshers and harvesters are designed to minimize grain loss and damage, ensuring that the harvested rice is of high quality. This can help farmers achieve better prices for their crops and increase their overall profitability.
Environmental Benefits
The use of machinery in rice farming can also have environmental benefits. For example, precision farming technologies such as GPS and automated steering systems can help reduce the use of inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. This can lead to more sustainable farming practices and reduce the environmental impact of rice farming.
Additionally, modern machinery is often designed to be more fuel-efficient and produce fewer emissions, further reducing the environmental footprint of rice farming operations.
Conclusion
The use of machinery in rice farming has revolutionized the way rice is grown, harvested, and processed. From tractors and plows to seeders, transplanters, harvesters, and threshers, these machines have significantly increased the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of rice farming operations.
By investing in modern agricultural machinery, rice farmers can reduce labor costs, improve crop quality, and adopt more environmentally friendly practices. As technology continues to advance, the future of rice farming looks promising, with even more innovative solutions on the horizon to help farmers meet the growing demand for this essential crop.