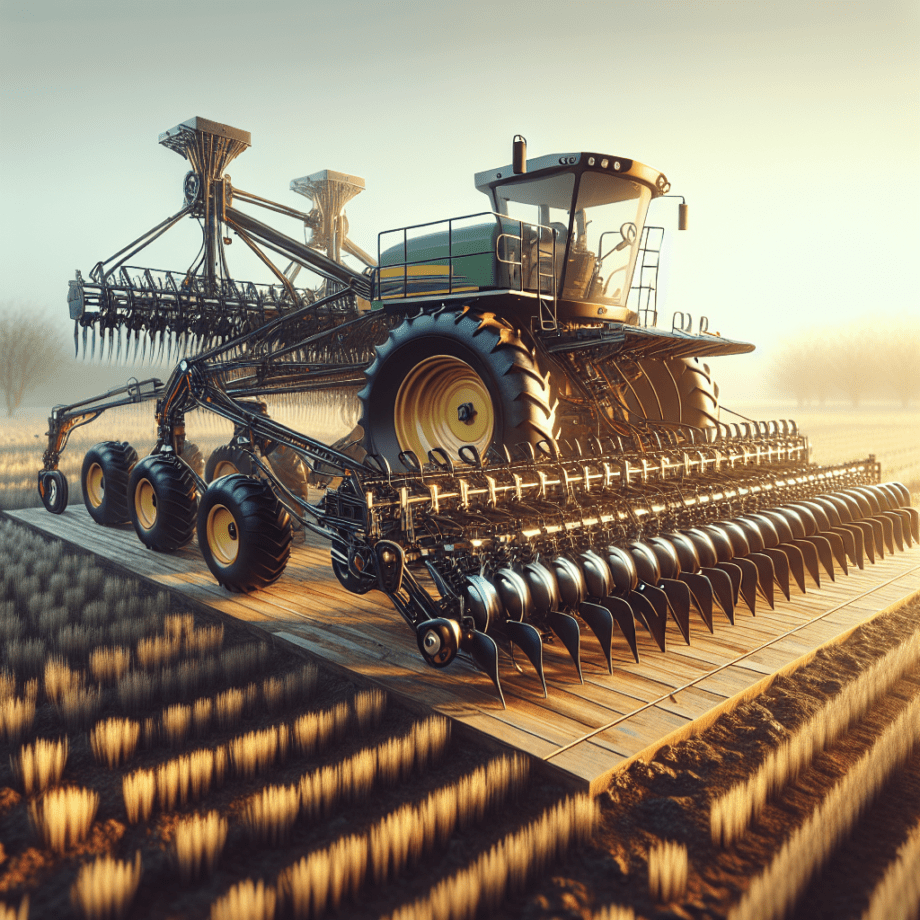
Understanding the differences between planters and seeders is crucial for optimizing agricultural productivity. Both machines play a vital role in the planting process, but they serve different purposes and are suited for different types of crops and farming conditions. This article delves into the specifics of each machine, their functionalities, and how to choose the right one for your farming needs.
Planters: Precision and Efficiency
Planters are specialized agricultural machines designed for precise seed placement. They are typically used for row crops such as corn, soybeans, and cotton. The primary advantage of using a planter is its ability to place seeds at a consistent depth and spacing, which is crucial for optimal crop growth and yield.
Functionality and Features
Planters are equipped with a series of components that work together to ensure accurate seed placement. These components include:
- Seed Metering System: This system controls the rate at which seeds are released from the hopper. It ensures that each seed is placed at the correct interval, preventing overcrowding and ensuring uniform growth.
- Seed Tubes: These tubes guide the seeds from the metering system to the soil. They are designed to minimize seed bounce and ensure that seeds are placed at the correct depth.
- Row Units: Each row unit is responsible for opening a furrow in the soil, placing the seed, and then covering it with soil. This ensures that the seed is in direct contact with the soil, which is essential for germination.
- Depth Control: Planters are equipped with mechanisms to control the depth at which seeds are planted. This is important for ensuring that seeds are placed in the optimal soil environment for germination and growth.
Advantages of Using Planters
There are several advantages to using planters for row crops:
- Precision: Planters offer unparalleled precision in seed placement, which is crucial for achieving uniform crop stands and maximizing yield.
- Efficiency: Planters can cover large areas quickly, making them ideal for large-scale farming operations.
- Versatility: Modern planters are highly versatile and can be adjusted to plant a variety of crops with different seed sizes and spacing requirements.
Seeders: Versatility and Simplicity
Seeders, on the other hand, are more versatile machines that can be used for a wide range of crops, including grains, grasses, and legumes. Unlike planters, seeders are designed to broadcast seeds over a wide area, making them ideal for crops that do not require precise row spacing.
Functionality and Features
Seeders come in various types, including broadcast seeders, drop seeders, and air seeders. Each type has its own unique features and functionalities:
- Broadcast Seeders: These seeders scatter seeds over a wide area, making them ideal for planting cover crops, grasses, and legumes. They are simple to operate and can cover large areas quickly.
- Drop Seeders: Drop seeders release seeds directly below the machine, providing more control over seed placement compared to broadcast seeders. They are often used for planting lawns and small grains.
- Air Seeders: Air seeders use a pneumatic system to distribute seeds evenly across the soil. They are highly efficient and can be used for a variety of crops, including cereals and oilseeds.
Advantages of Using Seeders
Seeders offer several advantages, particularly for certain types of crops and farming conditions:
- Versatility: Seeders can be used for a wide range of crops, making them a versatile choice for diverse farming operations.
- Simplicity: Seeders are generally simpler to operate and maintain compared to planters, making them accessible to a wider range of farmers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Seeders are often less expensive than planters, making them a cost-effective option for small to medium-sized farms.
Choosing the Right Machine for Your Farm
When deciding between a planter and a seeder, several factors should be considered to ensure that you choose the right machine for your specific needs:
Type of Crop
The type of crop you are planting is one of the most important factors to consider. Planters are ideal for row crops that require precise spacing and depth, such as corn and soybeans. Seeders, on the other hand, are better suited for crops that can be broadcast or drilled, such as grains, grasses, and legumes.
Farm Size and Scale
The size and scale of your farming operation will also influence your choice. Planters are typically more efficient for large-scale operations, as they can cover large areas quickly and with precision. Seeders, however, are often more suitable for smaller farms or for planting cover crops and pastures.
Soil and Field Conditions
The condition of your soil and fields can also impact your decision. Planters are designed to work well in a variety of soil conditions, including no-till and minimum-till systems. Seeders, particularly broadcast seeders, may be more affected by soil conditions and may require additional soil preparation to ensure even seed distribution.
Budget and Maintenance
Finally, your budget and maintenance capabilities should be considered. Planters are generally more expensive and require more maintenance compared to seeders. However, the increased precision and efficiency of planters can lead to higher yields and better overall profitability in the long run.
Conclusion
Both planters and seeders play essential roles in modern agriculture, each offering unique advantages and functionalities. By understanding the differences between these machines and considering factors such as crop type, farm size, soil conditions, and budget, farmers can make informed decisions to optimize their planting processes and achieve better yields. Whether you choose a planter for its precision or a seeder for its versatility, the right machine can make a significant difference in the success of your farming operation.